Brief introduction and application of parallel seismic transmitted wave detection technology
In the process of pile foundation inspection, besides the conventional underground pile foundation, it is sometimes necessary to inspect the length and integrity of foundation piles in deep foundation, foundation piles under bridge piers and existing buildings. At present, the equipment widely used in pile foundation detection mainly uses the reflected wave method, which can’t enter at the top of the foundation, or the pile is too long and thin (i.e., the length-diameter ratio of the pile is too large), there are foundation piles with serious defects in the shallow part of the pile body, and piles with low caps, etc., so the low strain reflected wave method can’t be used for testing. For the foundation pile, because the elastic wave transmitted from the pile body to the side hole has the advantages of short path and small interference, and can reflect the quality of the pile body below the defect and the position information of the pile bottom, it can evaluate the quality of the pile foundation more comprehensively and reliably than the commonly used reflected wave method.
Application
Parallel seismic transmitted wave method can be used not only for the detection of piles in construction projects, but also for the detection of piles in deep foundations, piles under piers and abutments, and piles under existing buildings, making up for the defects of low-strain reflected wave method, which is more widely used than traditional low-strain reflected wave method. PST(A) parallel seismic tester can be used not only to detect pile defects, but also to detect pile length, average wave velocity of pile body and wave velocity of bearing layer at pile bottom, so as to evaluate whether the integrity of foundation pile meets the design requirements.

Test Principle
Parallel seismic transmission method is to use a hammer (force bar) to strike vertically on the top surface of pile (or superstructure such as pile cap connected with the top of pile) to generate stress wave, which propagates downward along the pile body. As shown in Figure 1, it transmits when it meets the surrounding soil layer, and a sensor is placed in the hole drilled in advance next to the pile to receive the transmitted wave signal, thus reading the wave time at different depths and drawing the first arrival time-depth relationship diagram. When the sensor is lower than the pile bottom, the sound velocity will change, and an inflection point will be displayed on the time-depth diagram. The length of the pile can be inferred from the position where the slope of the straight line changes. The slopes of the two straight lines can be used to infer the average wave velocity of the pile body and the wave velocity of the bearing layer at the pile bottom.
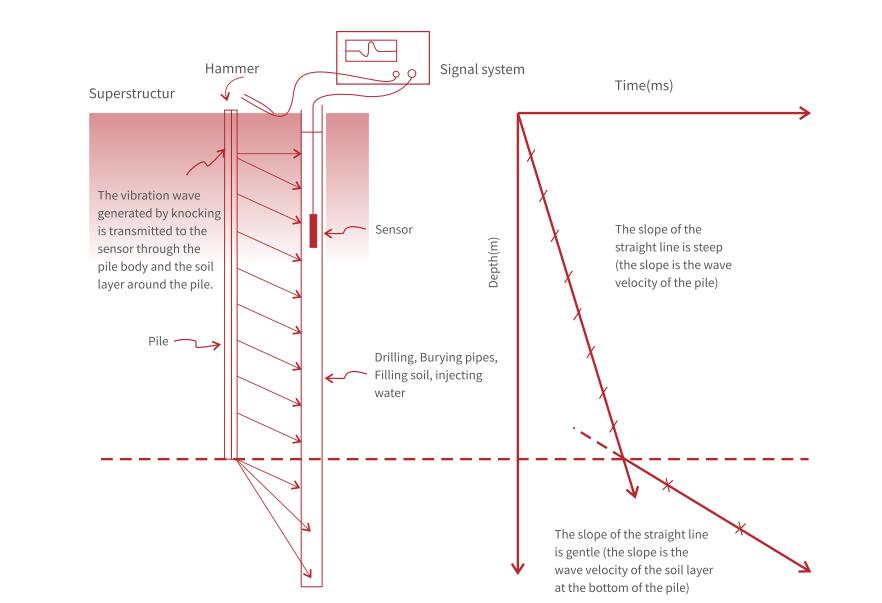 Schematic diagram of the principle of parallel seismic transmitted wave method
Schematic diagram of the principle of parallel seismic transmitted wave method

